Traditional QCM technology is limited to characterization of thin and rigid films. This limitation, and the possibility to characterize soft or thick films has been addressed with extended QCMs, such as QCM-D, which also measure the energy losses. Here we explain how QCM-D works.
Quartz crystal microbalance with Dissipation, QCM-D, is based on the same working principle as QCM, i.e. it measures the resonance frequency changes, Δf, of a quartz crystal as a function of time. In addition to the frequency capture, QCM-D also collects time resolved information about the energy losses, the dissipation. I. e. QCM-D collects Δf and ΔD as a function of time, Fig 1, whereas QCM collects Δf as a function of time.
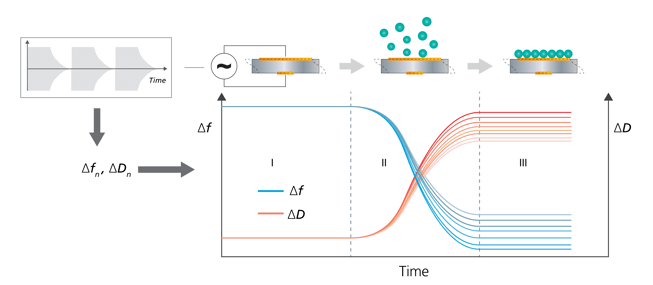
Figure 1. The figure shows a schematic illustration of the working principle of QSense QCM-D, a multi-harmonic QCM-D, which via so-called pinging provides time resolved information on f and D at multiple harmonics. Via a rapid, periodic excitation of the driving power (upper left), the oscillation frequency, f, and the decay time, which is inversely proportional to D, can be captured and thereby, time-resolved information of changes in Δf and ΔD can be plotted as molecules interact with the sensor surface. In the schematic adsorption scenario and plot, section (I) shows a bare surface and stable baselines of multiple Δf:s and ΔD:s. Period (II) shows how molecules bind to the surface, and as a result, the frequencies decrease and the dissipations increase, indicating mass uptake and increasing energy loss. Period (III) shows how the surface uptake has been completed and the frequency and dissipation responses have stabilized. The collectyed QCM-D data can be used for viscoelastic modelling and quantification of mass, thickness and viscoelastic properties of the adsorbed layer.
The benefit of measuring the dissipation in addition to just the frequency, is that you get information on whether the layer at the sensor surface is rigid or not, and if the Sauerbrey equation can be used for the quantification of mass. Also, if f and D are collected at multiple harmonics, it is possible to apply viscoelastic modelling on the data.
QCM-D technology measures two parameters in parallel, the resonance frequency, f, and the dissipation, D.
QCM-D:s currently in the market measure the dissipation either via the bandwidth, or via measuring the oscillation decay time after the driving power has been switched off, so-called pinging. QSense QCM-D is based on the pinging approach.
Download the overview to learn more about QCM-D technology and how it works.
Read the guidelines on how to decide which QCM instrument will be the most suitable for your needs
Read about how protein adsorption at various surface and solution conditions quickly can be measured
Read about what single-harmonic and multi-harmonic QCM-D means and what the difference is between these instruments.
Read about how QSense QCM-D analysis is used as a powerful tool to investigate protein-lipid nanoparticles binding affinity
Learn about the difference between the theoretical QCM sensitivity and the sensitivity which is relevant in a measurement situation.
Read about the piezoelectric effect and how piezoelectricity arises
Learn more about QSense 4th generation QCM-D platform which provides a sharper tool in the scientist toolbox and simplifies data interpretation.
Learn about how biointerfaces and biomolecular interactions can be studied using QSense® QCM-D and what information these measurements offer.
Read about Prof. Jackman's experience using QCM-D to study surfactant-interaction with model membranes
Sign upp for the webinar to learn more about how QCM-D is used to study biomaterial-induced activation of the immune system
Learn about what aspects to consider after you have run a QCM measurement
